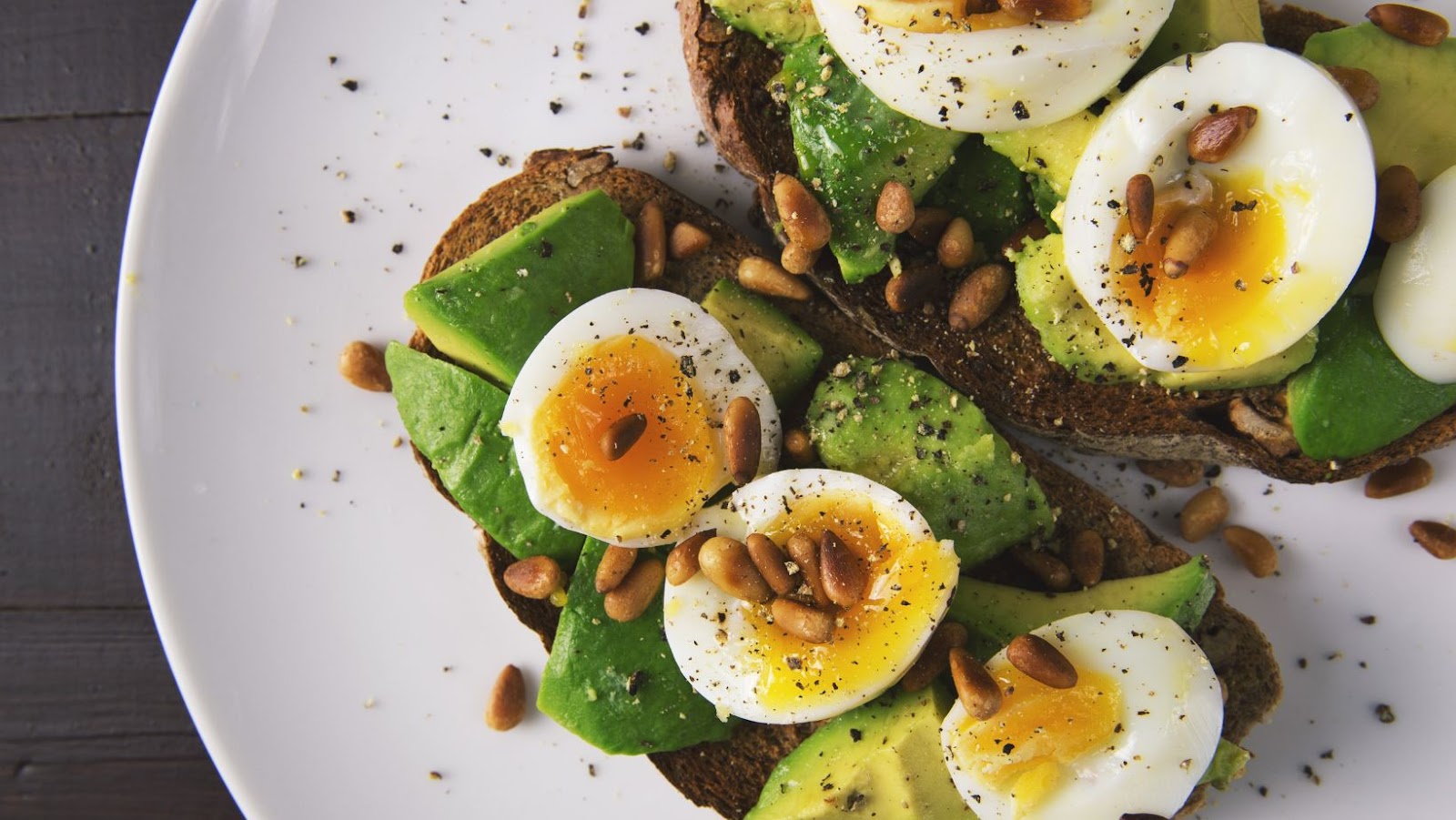
The ketogenic (keto) diet is a popular low-carb, high-fat weight loss plan that can help you achieve your weight loss and health goals. It has been shown to be helpful in improving cardiovascular health, decreasing inflammation, and regulating blood sugar. A central part of the keto diet is eating plenty of eggs. Although eggs are a rich source of healthy fats and proteins, there are some risks associated with consuming them in large amounts or on an ongoing basis. By understanding the possible risks and taking steps to limit your intake, you can ensure that eggs become a healthy part of your keto diet. This article provides an overview of the potential risks associated with eating eggs on a keto diet as well as advice on how many eggs you should eat each day.
How many eggs a day on a keto diet
Eating eggs on a keto diet can provide numerous health benefits, including improved heart health and weight loss. Eggs are extremely rich in protein, healthy fats, essential vitamins, and minerals. They make a great breakfast choice on a keto diet and can be easily prepared in various ways. But each person should consider how many eggs they should eat daily before getting started. Let’s discuss the possible risks associated with eating too many eggs on a keto diet.
Overview of the Keto Diet
The ketogenic diet (also known as the “keto diet”) is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that has become increasingly popular in recent years. By eliminating almost all carbohydrates, the keto diet forces your body to burn fat for energy rather than glucose. This typically results in weight loss and other health benefits. In this article, we’ll take a look at how many eggs you can safely eat on a keto diet.
What is the Keto Diet?
The ketogenic, or keto, diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate diet that has become one of the most popular nutrition trends in recent years. Unlike the traditional low-carb diets recommended for weight control and blood sugar management, the keto diet emphasises the elimination of all carbohydrates from the diet and replaces them with healthy fats. The downside is that it can be difficult to adhere to long-term.
The macronutrient makeup of a person’s carbohydrate intake on a keto diet should consist mainly of fats (75%-90%), protein (10%-20%) and minimal carbohydrates (<10%). This type of eating pattern should limit carbohydrates so much that your body begins burning fat for energy, putting you into a state of “ketosis”. Ketosis occurs when carbon atoms from fatty acids are used to create energy instead of glucose from carbohydrate metabolism.
The most important factor when considering this type of extreme eating pattern is to keep total nutrient balance in mind; focus on whole foods with minimal processing and limit processed foods with added sugars and unhealthy fats. Additionally, adequate hydration should always be maintained with plenty of fluids throughout the day; water, naturally brewed and unsweetened tea or coffee are all excellent choices.
When following the keto diet correctly – i.e., making sure total calories consumed are appropriate for your individual goals – eating eggs can be beneficial as they contain essential nutrients like vitamins A, B12, B2, selenium as well as healthy fats like omega-3s. How many eggs you should eat per day depends on an individual’s calorie requirements but recommendations advise those on a very low carbohydrate (ketogenic) diet should strive to consume no more than two per day while those eating more moderate amounts might enjoy up to four eggs daily.
Benefits of the Keto Diet
The keto diet offers many health benefits such as weight loss, improved mental clarity, lower cholesterol levels, better control of type 2 diabetes, and a reduction in risk for heart disease. It is an eating pattern that focuses on reducing the amount of carbohydrates and sugars in the diet and replacing them with high-fat foods that provide a lot of energy.
Specific benefits associated with keto include increases in energy levels due to higher fat content, better mental clarity due to fewer carbohydrates in the diet which can help focus and cognitive performance, balanced hormones due to the reduction in inflammation caused by consuming less sugar, better digestion due to increased fibre intake, and reduction of specific cancers due to lower levels of sugar intake. Additionally, when followed as prescribed, it has been proven to consistently lead to weight loss.
Although there are many nutritional benefits associated with the Keto diet including providing essential energy sources found in fat content while reducing overall deprivation caloric-wise it is important to note that there are still some risks associated with this eating pattern. Common side effects include fatigue during initial adaptation period due to electrolyte imbalance from redirection of fuel sources from carbohydrates to ketones as well as potential health risks including liver damage and kidney stones if followed improperly for an extended period of time or without proper medical support/consultation.
While eating eggs on a Keto diet does have its inherent nutritional value including protein for growth/repair and triglyceride structure (omega-3) for immunity etc., if not careful it is easy for one’s daily caloric intake can be dependent on egg consumption leading potential health risks from affecting cholesterol levels (due higher saturated fat) causing cardiovascular side effects when consumed over long periods. Therefore it is recommended by health professionals that individuals limit their egg consumption while following Keto dietary plans to no more than 3-4 eggs per day or equivalent other low carb food items like vegetables/fruits or cheese along with limited saturated fats sources like butter/margarine etc.
Risks of Eating Too Many Eggs on a Keto Diet
Eggs are a staple of many ketogenic diets, as they are a great source of healthy fats and protein. While they are a beneficial part of this diet, there are some risks associated with eating too many eggs on the keto diet. Too many eggs can lead to an imbalanced macronutrient ratio, resulting in an unhealthy diet. In addition, eating too many eggs can cause digestive issues and nutrient deficiencies. We will explore these potential risks in this article.
Cholesterol
Chilli burn Extra care must be taken when consuming eggs on a keto diet. Although Eggs may seem harmless, they contain a high amount of cholesterol, which can put individuals at risk for developing heart disease. Each egg yolk contains approximately 212 mg of cholesterol, so if an individual is eating multiple eggs each day and not taking care to balance out the rest of their diet with healthy sources of fat, such as olive oil, avocados and nuts, it can increase their intake to dangerous levels. Excessive cholesterol intake can also lead to an increased risk of gallbladder disease and stroke. That’s why limiting your egg intake is critical for maintaining a healthy balance at all times.
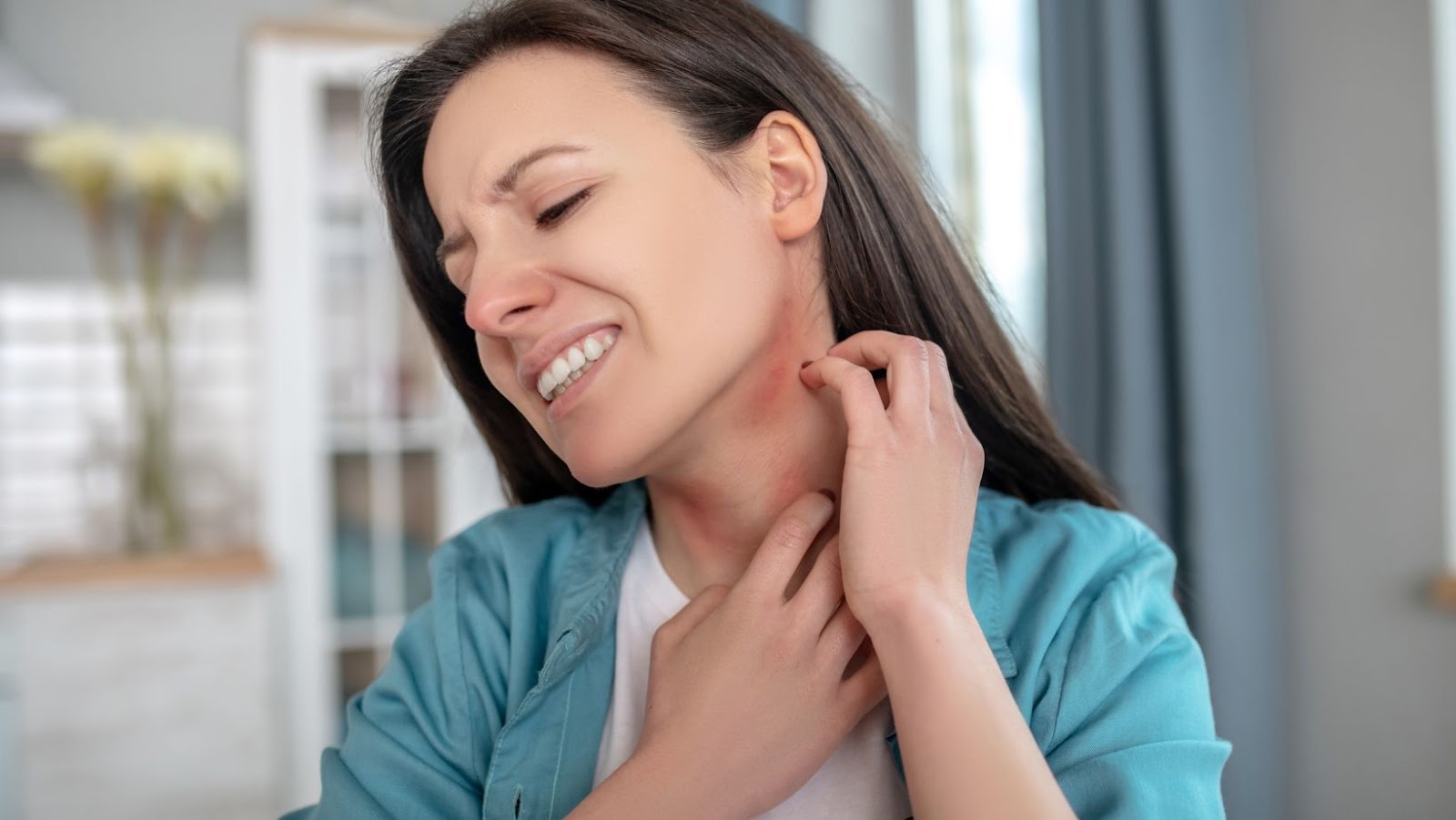
Allergies
The ketogenic diet is a high-fat, low-carbohydrate meal plan that can help you lose weight and improve certain health conditions. Eggs are often included in keto diets because they contain healthy fats and proteins with minimal carbohydrates. While Eating eggs on a regular basis can help you keep within your daily carbohydrate requirements, eating too many eggs runs the risk of allergies or intolerance.
Some people have sensitivities to the proteins in eggs and may experience symptoms such as nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps or diarrhoea after eating them. For this reason it’s important to monitor how much you’re consuming regularly so that you don’t exceed your daily limit.
If you have a history of egg allergies it is best to avoid eating eggs altogether as a precautionary measure. If you don’t have an allergy or intolerance but find that you experience digestive discomfort, cut down on your egg consumption or look for other sources of protein that are more agreeable with your system. According to studies conducted by the Harvard Medical School Department of Nutrition, an adult should consume no more than 2-3 whole eggs per day while following a keto diet and not consume any additional yolks beyond this amount.
Contamination
Eating too many eggs on a ketogenic diet can pose a risk of contamination due to its high-fat, low-carb content. High-fat foods like eggs can easily become contaminated with salmonella, E. coli and other bacteria if left at room temperature for too long or if stored improperly during preparation or transport. It is important to take precautions in selecting, preparation and storage of eggs for maximum safety.
Additionally, individuals following a strict ketogenic diet that consumes higher levels of fat should ensure that they are consuming enough beneficial polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) from sources such as fish oil and other animal sources, as the higher consumption of saturated fats on this type of diet can increase levels of bad cholesterol and lipid markers associated with heart disease risk factors. Eating too many eggs can lead to an imbalance in essential fatty acids impacting overall health.
Recommended Egg Intake
Eggs are an important source of protein, healthy fats, vitamins and minerals when following a keto diet. While the exact number of eggs you should eat will depend on your specific nutritional requirements, the general recommendation is to include at least three eggs per day. The egg yolk contains a good proportion of saturated fats, which can help boost your overall fat intake; however, it’s important to limit consumption of egg whites due to their high carb content.
Including plenty of other whole foods in your diet such as avocados, fatty fish, grass-fed meat and full-fat dairy products can enhance the nutritional benefits from eggs on a keto diet. It’s also advised that you opt for free-range organic eggs due to the omega 3 fatty acid content.
As with any dietary approach, it’s important to ensure that you are eating a balanced variety of nutritious foods while following a keto diet; this includes monitoring total daily calorie intake and individual nutrient sources. Eating too many eggs could lead to an unhealthy level of cholesterol in the body if consumed without making adjustments to other food choices within your daily routine. For example, you might consider reducing consumption of saturated fat or processed meats if eating too many eggs on a regular basis as well as adjusting serving sizes accordingly.
Egg Substitutes
Eggs are a key part of the ketogenic diet, however not everyone enjoys eating them or is allergic to eggs. Luckily, there are some great egg substitutes that can help provide similar benefits without having to add eggs into the diet. Here is a list of egg alternatives that are keto-friendly and can be used in many recipes:
-Flaxseed meal – A tablespoon of ground flaxseed and three tablespoons of water create an egg-like substance when mixed together. A common vegan replacement for eggs in baking as it has binding properties and a good source of fibre.
-Chia seeds – A tablespoon of chia seeds mixed with three tablespoons of water create an egg-like consistency similar to linseed or ground flax seed and can also be used as an egg replacement in baking recipes.
-Almond flour – Almond flour combined with almond or coconut milk, lemon juice, and apple cider vinegar works well as an egg substitute for frittatas, quiches and other baked goods .
-Bananas – Pureed banana works great with baking recipes like muffins and breads due to its moistening qualities, allowing more tenderness in these products while also providing some sweetness.
-Aquafaba – This is the liquid part (or “brine”) from canned chickpeas that has strong binding properties making it perfect for vegan omelettes or mock meringue desserts.
In conclusion, eggs can be a beneficial part of a keto diet if they are consumed in moderation. Eating up to three eggs a day is generally accepted as safe and benefits may be seen if this moderate intake is used in conjunction with other healthy dietary practices. As with any dietary choice, consulting a qualified medical professional is recommended before making changes to your diet. Eating in moderation and listening to your body will help ensure that you receive the nutrition you need without any adverse effects.