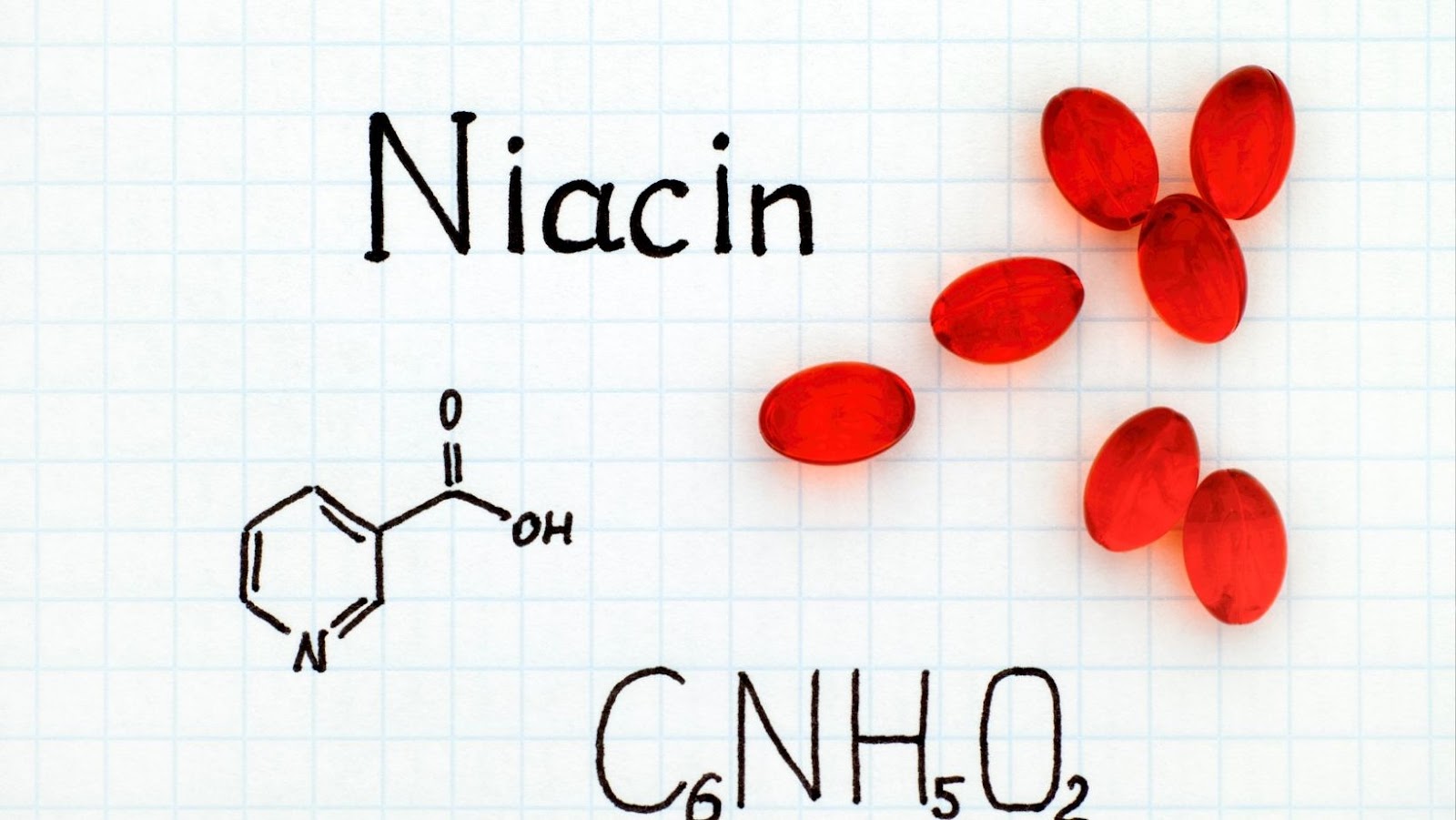
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin that forms part of the B-complex vitamins. It is also known as nicotinic acid and the form of niacin found in supplements and fortified foods is called “niacinamide” or “nicotinamide.” Niacin is an essential vitamin because humans cannot make it. It must be obtained from food or dietary supplements.
Niacin where to buy
Niacin plays critical roles in energy metabolism and healthy cellular function, supporting healthy nerve tissue functioning, as well as healthy skin, hair, eyes and liver. Deficiencies in niacin can lead to pellagra, a condition marked by dermatitis, digestive disturbances and neurological issues like dementia.
It has long been known for its ability to elevate low levels of “bad” cholesterol (LDL-cholesterol) and triglycerides making it the preferred choice for people who suffer from high cholesterol levels. However, taking niacin comes with some potential adverse effects if taken at high doses so it is important to understand how it works as well as what precautions need to be taken when using this supplement.
What is Niacin?
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is an essential nutrient and a common dietary supplement with many use cases. It’s naturally found in foods like meat, fish, nuts, and grains. It’s also a popular vitamin supplement that is available over the counter or via prescription doses.
Niacin plays an important role in numerous processes in the body including energy metabolism and cell function. Supplemental forms are often used to treat certain medical conditions such as high cholesterol, ageing skin problems such as psoriasis or age spots, or digestion issues like heartburn. This supplement can also be used for depression and anxiety-related issues.
It’s important to take niacin with proper guidance from a doctor or dietitian before taking this supplement. There are some side effects and precautions associated with taking niacin supplements that you should be aware of before buying it. This article provides information about these potential side effects and how to buy the right product for your needs.
Benefits of Niacin
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is a water-soluble nutrient found naturally in many foods such as nuts, fish, and legumes. Niacin plays an important role in overall health and is known to have numerous benefits, such as reducing cholesterol levels, improving cardiovascular health, and helping to regulate blood sugar levels. In this article, we take a closer look at the many benefits of niacin.
Lower cholesterol levels
One of the primary benefits of niacin is its ability to help lower levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, also known as “bad” cholesterol. LDL cholesterol is associated with an increased risk for heart attack and stroke. Niacin helps raise levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL), which is considered “good” cholesterol, in the blood. By pushing up good cholesterol levels and decreasing bad cholesterol, niacin can help improve cardiovascular health and even reduce stroke risk. It’s important to note that this effect has been documented when taking doses up to 2 grams per day. Keep in mind that higher doses may produce other side effects or risks which should be discussed with your healthcare provider before starting a larger dose regimen.
Treat diabetes
Niacin may help protect people with diabetes against the development of cardiovascular disease. One way it might do this is by improving the levels of “good” cholesterol (HDL) in the blood. High HDL levels can help prevent fatty buildups within the arteries, which can lead to cardiovascular issues. Research indicates that niacin may also reduce inflammation, which can help lower the risk of further damage to the heart and other organs in people with diabetes.
Niacin has also been found to improve glycemic control, which is associated with a reduced risk of cardiovascular events and mortality in diabetes patients. It may also help lower fasting blood sugars and improve insulin sensitivity.
However, patients with diabetes should not take niacin supplements without discussing it first with a doctor who understands their overall treatment plan for managing their diabetes and its potential complications. People taking niacin as part of treatment should be closely monitored by their doctor, because high doses are associated with serious side effects such as liver damage or digestive problems.
Improve brain function
Niacin (also known as vitamin B3) is an important nutrient for brain health. It has been shown to improve memory, increase focus and concentration, and protect cells from damage caused by free radicals. Niacin can also decrease inflammation in the brain, which can lead to improved cognitive performance. It may even help prevent neurological diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
Niacin helps boost production of neurotransmitters like serotonin, norepinephrine, and dopamine. These chemical messengers are essential for communication between neurons in the brain. They are responsible for sending messages between different areas of the brain which help with memory and learning.
Studies have also shown that niacin may be beneficial in treating depression due to its effects on neurotransmitter levels. It has been found that niacin can improve mood by increasing serotonin levels in the brain. Additionally, niacin has been found to improve overall energy levels and reduce fatigue associated with depression.
Finally, niacin can also help protect your brain from damage caused by free radicals or oxidative stress due to its antioxidant properties. Oxidative stress is linked to Alzheimer’s disease, so protection against it could be beneficial for overall health and longevity of the brain cells.
Side Effects of Niacin
Niacin is a vitamin found naturally in foods and also available as a dietary supplement. As beneficial as niacin is for the body, it comes with certain side effects and precautions. Although mild side effects are common with niacin, more severe effects can occur in some people. It’s important to understand the potential side effects in order to make an informed decision about whether or not to take this supplement. Let’s take a closer look at the potential side effects of niacin.
Flushing
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is an essential vitamin involved in energy production and metabolism. It’s important for a number of body functions and is available in dietary supplements and various food sources. While niacin is generally safe in moderate doses, it can cause side effects like flushing.
Flushing is the most common side effect of niacin use and occurs when blood vessels dilate and cause warmth or redness on the skin’s surface. This often occurs within minutes of taking a dose of niacin. Flushing can last anywhere from 20 minutes to two hours after taking the supplement, although for some people it may take up to four hours for the symptoms to completely disappear. Other symptoms associated with flushing may include itching or tingling, nausea and headache. In rare cases, prolonged flushing due to niacin use may rapidly progress to swelling of the face and tongue or chest pain throughout the body. This should be reported to a healthcare provider immediately if it occurs.
Those who experience any side effects associated with niacin use should consult their healthcare provider regarding further treatment options or modifications to dosage regimens if necessary. Niacin is available over-the-counter in many forms including tablets, capsules, sustained release tablets and slow release capsules — make sure that you select products manufactured by reputable suppliers as low-quality supplements have been linked with adverse events when taken at higher than advised doses.
Upset stomach
Upset stomach is the most common side effect of niacin when taken in high doses. It typically presents as cramping, abdominal discomfort, nausea and/or vomiting. This side effect can be managed by taking smaller doses over time or taking the niacin with food. If you experience any signs of an allergic reaction such as hives, rash, difficulty breathing or swelling of the mouth or throat, discontinue use and seek medical advice from a healthcare professional immediately.
Niacin can cause an increase in blood sugar levels in people with diabetes and may interact with some medications such as blood thinners and cholesterol-lowering drugs like statins. Consult your doctor before taking niacin if you have a pre-existing medical condition to avoid any complications and adverse reactions. Niacin should also not be used by children unless otherwise advised by a doctor as it may interfere with their growth and development. When buying niacin supplements, always read labels carefully to make sure they do not contain additional ingredients that may cause unwanted side effects or interact with medications you are already taking.
Liver damage
Niacin is an important nutrient and vitamin, however, it comes with some side effects that should be addressed. One of the main side effect risks associated with niacin use is potential damage to the liver. Due to its enzyme-modulating abilities, niacin can cause abnormalities in liver function that can rupture if left unchecked.
In patients who have no pre-existing liver damage or issues prior to taking niacin, it’s commonly safe, however, those who already have a weakened or damaged liver could see even more harm through ingesting higher dose supplements or consuming any form of enriched food such as processed grains or breakfast cereal bars and other fortified foods.
The U.S Food and Drug Administration requires all dietary supplement labels to warn consumers about potential severe liver complications due to higher doses of niacin associated with cardiovascular disease prevention treatments. They suggest individuals consult a doctor before beginning any high dose regimen in order to rule out any underlying causes of possible liver damage prior to supplementation. Additionally, they advise anyone taking regular medications including certain cholesterol medications (such as lovastatin and simvastatin) refrain from consuming high doses of niacin without a medical prescription as these two drugs taken together increase the risk for severe adverse reactions within this system organ due to overstimulation caused by enzymes in the body interacting differently than would be usual for a single alone drug intake.
Skin rash
When taken in large doses, niacin can cause a skin rash known as cutaneous vasodilation—a sign that the blood vessels near your skin are rapidly and excessively expanding. This rash may be accompanied by itching, flushing and burning sensations. Some people who take large doses of niacin develop peeling of the skin or other allergic reactions to the vitamin supplement. If you experience any side effects when taking niacin supplements, it is important to discontinue use and speak with a healthcare professional as soon as possible.
Precautions
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin found in foods such as fish, meat, nuts, and some fortified cereals. Niacin can also be taken in the form of dietary supplement or as part of a multivitamin. It’s important to remember that niacin should be taken with caution and be aware of potential side effects. In this article, let’s look into some precautions and side effects of taking niacin.
Consult a doctor before taking niacin
Before taking niacin, it is essential to consult a doctor to ensure that it is safe for you. Your doctor can evaluate your medical history and current health condition and decide if niacin is suitable for you or not.
Individuals who have kidney disease, gout, liver disease, diabetes, certain types of heart disease (angina) should talk to their doctor before taking niacin. Some people might experience adverse effects from niacin if used in high doses such as skin flushing, fatigue, nausea, vomiting and stomach pain which could be more severe in individuals with underlying health conditions.
It is also important to talk to a healthcare professional before taking any other medicines along with niacin as it may increase the risk of side effects. Several drugs interact with niacin including some of the statins (simvastatin/lovastatin) used to lower cholesterol level as well as antidiabetic drugs (metformin). Therefore, it’s necessary to review all medications taken regularly and consult your healthcare provider before using any new drug while on niacin supplement.
In addition, pregnant or breastfeeding women should not take any form of supplement including niacin without consulting their doctor first since the safety has not been established in these populations. To ensure safest use of supplements or medications related to health issues like cholesterol or diabetes management, proper consultation with qualified medical personnel is required prior usage each time.
Do not take niacin if you are pregnant or breastfeeding
Niacin should not be taken during pregnancy or while breastfeeding unless recommended by a healthcare provider. It has not been established as safe to use during these times and may pose a risk to the developing baby. If you are pregnant or have recently given birth, speak with your doctor before taking niacin.
Niacin can pass into breast milk and may cause side effects in breastfed babies. As such, it is important that women who are breastfeeding discuss taking the supplement with their doctor before doing so. Breastfeeding moms should monitor their baby for any signs of side effects, such as skin flushing, rash, upset stomach or diarrhoea. If any of these occur, stop taking niacin and contact a healthcare provider immediately.
Monitor your liver function
Niacin can cause liver damage and there are increased risks for those with existing liver or gallbladder conditions. To reduce the risk of experiencing adverse effects, any potential side effects should be monitored when using niacin supplements.
You should tell your doctor or healthcare provider if you are taking niacin supplements before having any tests, as niacin can interfere with lab results. Your doctor may require that you have a complete physical and do blood tests to monitor your liver function before and after taking niacin supplements. Regular lab testing may also be necessary during use of the supplement to watch for unexpected changes in your liver enzymes.
Where to Buy Niacin
If you are looking to purchase niacin, you should be aware of the side effects and precautions that accompany it. Niacin is available in a variety of forms, from over-the-counter supplements to prescription medications. It is important to know where to buy niacin and what precautions you should take before taking it. In this section, we will discuss the best places to purchase niacin, the side effects it can cause, and precautions you should take before using it.
Online retailers
Niacin is a water-soluble vitamin found in many fruits, vegetables and proteins. Because niacin is an essential nutrient, it can be purchased without a doctor’s prescription from online retailers. When looking for niacin supplements online, it is important to select products from reliable sources and take into account the potential side effects of niacin.
Supplements sold online are generally available as capsules or tablets containing niacinamide (known as inositol hexanicotinate), although sustained release forms of niacin powders can also be purchased from some retailers. The majority of well-known supplement companies sell both capsule and tablet form, with different dosage strengths ranging from 50-500 mg being available.
Before buying a supplement, consider the potential side effects associated with taking too much niacin, such as flushing (heat and redness in the face), digestive upset/diarrhoea, nausea/vomiting and itching/rash. Additionally, individuals who take certain medications or have health conditions such as liver disease should avoid taking high doses of this vitamin or speak to their doctor before adding it to their diet. As always, it is best to check the safety label on each product before making a purchase
Pharmacies
Niacin, or nicotinic acid, is an essential nutrient that’s naturally found in some foods and available as a dietary supplement. It helps in the conversion of certain nutrients into energy and has been used medicinally to treat high cholesterol and other conditions.
If you’re looking for where to buy niacin, pharmacies are one of the best options. In most cases, pharmacies will carry niacin in both pill form and powder form. Pill forms come in various strengths – from low-dose tablets of 100 mg to high-strength tablets of 1,000 mg. Be sure to read the label carefully when selecting a product; some products may also contain other ingredients such as magnesium stearate or calcium phosphate. Additionally, you should always check with your doctor first before taking any type of nutritional supplement.
It’s important to take niacin only under a doctor’s supervision because too much niacin can cause serious side effects such as flushing, dizziness, headache, itching and nausea. If you experience any of these symptoms after taking niacin, it’s important to stop use immediately and consult your physician for further evaluation and treatment.
Health food stores
Niacin is a member of the B-vitamin family and it’s an essential nutrient for human health. It comes in two forms: nicotinic acid (niacin) and niacinamide. There are many benefits of niacin, such as reducing cholesterol levels, treating pellagra, improving blood sugar control, treating skin conditions and improving cognitive function.
The best place to buy niacin is at health food stores or through online retailers. Niacin tablets, capsules and powders can be found at drug stores and natural health outlets. The best sources of niacin come from foods such as tuna, beef liver, salmon and avocados as well as processed grains and cereals that contain added niacin.