What’s on your plate? It’s a question we often ask, but do we really know what’s in our food? I’m not talking about the ingredients listed on the package, but the unseen elements that sneak into our meals. Chemical residues, for instance, can find their way into our food chain, posing potential health risks.
Enter the world of chemical residue testing in food safety. This unsung hero plays a crucial role in ensuring what we consume is safe and free from harmful substances. It’s a fascinating field, blending science, technology, and a dash of detective work to protect our plates.
Understanding Chemical Residue Testing
In the realm of food safety, chemical residue testing stands as an essential player. Paramount in separating safe food products from risks, this type of testing carries out a critical task.
The Scope of Chemical Residue Testing
Chemical residue testing isn’t limited to finding mere leftovers of pesticides or herbicides on the surface of fruits and vegetables. It delves deeper, inspecting a host of substances. It takes a hard look at veterinary drugs found in meat and dairy, scrutinizes mycotoxins in grains, and keeps an eye out for heavy metals in seafood. In diverse food groups, contaminants vary. So does the domain of chemical residue testing. It spans across numerous food categories, extending its services to grapple with different forms of potential contamination.
Why Chemical Residue Testing Matters
One might ask, why does chemical residue testing bear such importance? Known or unknown, residue of chemicals in the food we consume can spell harm for our health. Immediate exposure may trigger allergic reactions or food poisoning, but it’s the long-term effects that cast a graver concern. Chronic conditions such as heart disease, liver damage, and an assortment of cancers lurk behind continual consumption of food tainted with certain chemical elements. That’s where chemical residue testing steps in, sifting out contaminants and affirms safety, upholding the quality of food products in the market against potential public health risks. Consequently, our trust in the food we eat is, in part, the fruit of dedicated and accurate chemical residue testing.
The Process of Chemical Residue Testing
In the world of food safety, chemical residue testing holds a vital role. But, what exactly is the process about? Specifically, it involves several steps to ensure accurate results.
Sample Preparation
Firstly, the testing process begins with sample preparation. Let’s say, for instance, from a crop.
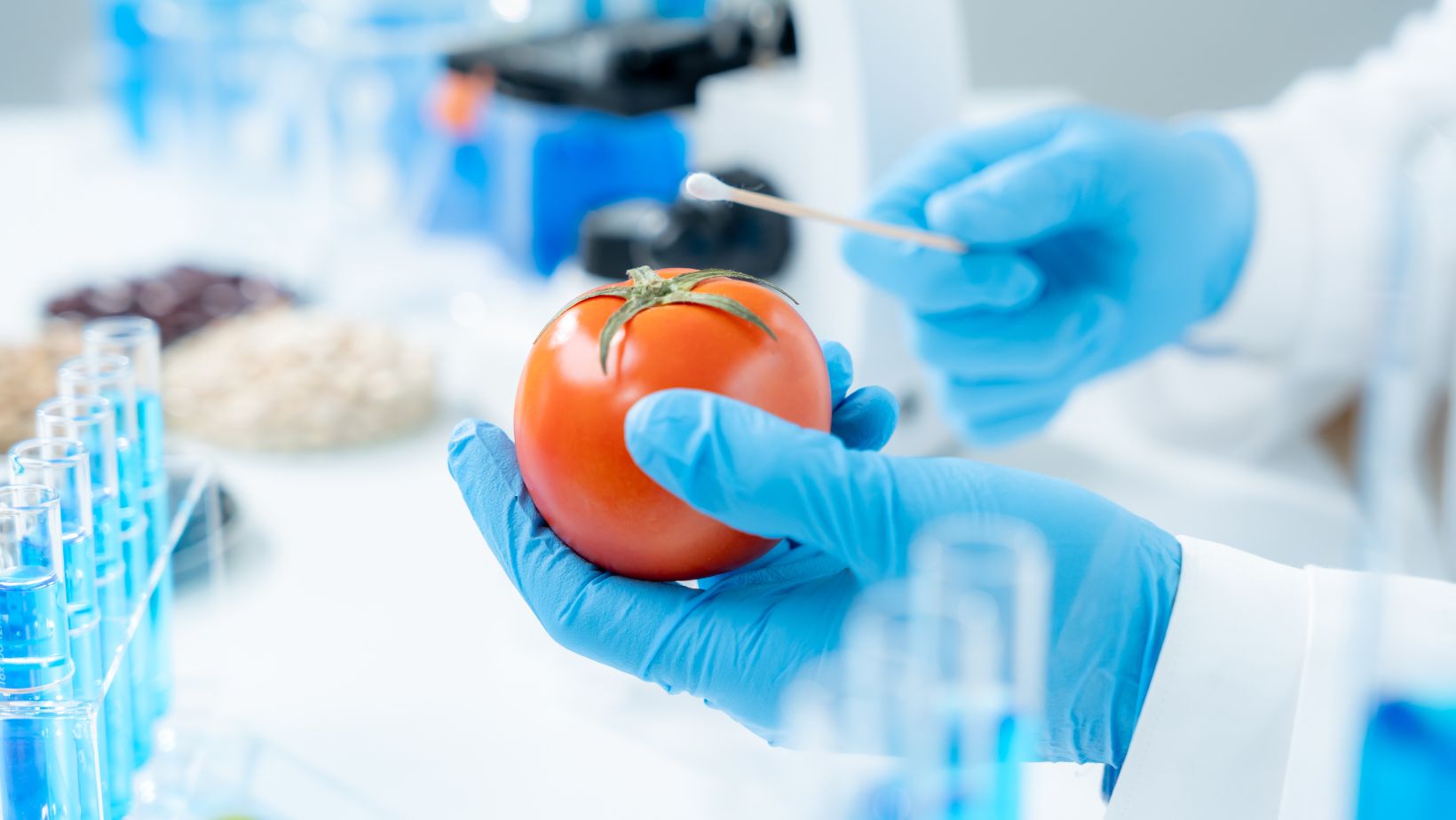

The crop is first washed, dried, and blended into a homogenous sample. This uniform sample then moves to the extraction phase.
Extraction
Extraction, the next phase, separates the chemical residues from the sample. This process typically includes solvents, often organic, that target certain types of residues. A good example would be acetonitrile, often used to extract residues in fruits and vegetables.
Analysis
Once the extraction phase is complete, the sample proceeds to the analysis component. In this phase, advanced technologies, such as Liquid Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) and Gas Chromatography – Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS), are utilized to detect and identify chemical residues.
Quantification
Finally, the chemical residues identified are quantified. This step determines the concentration of chemicals in the product. Laboratories typically use reference standards, substances with known concentration of residues, to measure the level of residue in the sample.
I’d like to remind you that the process might slightly vary depending on the type of food and the contaminants targeted. For instance, in meat or dairy products, the sample preparation may include additional steps to remove fats. Regardless, the core process remains the same, all dedicated to ensuring food safety and quality. Remember, food testing is not just about detecting contaminations. It’s about ensuring that each bite you take is safe and that public health gets its deserved protection.
The Role of Regulatory Agencies
Being the safety net against hazardous contamination, regulatory agencies work meticulously. They’re the ones instituting guidelines for chemical residue limits in food. Restrictive directives are set to avoid excessive chemical content, where exceeding the established limits can result in food becoming unsafe for consumption.
For instance, the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) determines pesticide tolerances, the maximum residue level permissible in food. If residues bypass the set tolerance, regulatory action becomes a necessity for safeguarding public health.
Similarly, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) in the U.S coordinates extensive food testing. They’re vested with the power of monitoring domestically produced and imported foods for residue compliance. Predominantly, field examinations and laboratory analysis form components of the FDA’s compliance program.
Quite often, agencies collaborate with food producers and retailers in a joint effort promoting food safety. An instance would be the Food Quality Protection Act (FQPA), enacted by the U.S. EPA. This act necessitates reasonable certainty of no harm from diet exposure to pesticide residues.
Advances in Chemical Residue Testing
Stemming from the advent of innovative technology, advances in chemical residue testing now make food testing more accurate and efficient. A notable progress lies in screening methods, now able to detect a wider spectrum of chemical residues in food. For example, Multi-residue methods (MRMs) gain traction, capable of detecting multiple contaminants in one single test.
Another leap forward can be observed in detection technology. Sophisticated instruments such as Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (GC-MS) and Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry (LC-MS) demonstrate significant strides in separating and identifying chemical residues. These strides matter since they increase the chance of detecting contaminants, saving time, and reducing costs.

Not to be overlooked is the development of rapid testing kits in the realm of food testing. These kits employ innovative technology to expedite the testing process. Take the ELISA (Enzyme-linked Immunosorbent Assay) kits, for instance. They enable quick, on-site testing, which is beneficial when monitoring food safety in real-time situations.
The Future of Chemical Residue Testing
Looking forward, I envision significant changes in the field of chemical residue testing in food. The evolution of technology is propelling the development of more advanced, quicker, and cost-efficient testing procedures, revolutionizing food safety as we know it. Let’s delve into some of these innovations poised to shape the future of this crucial sector.
Firstly, the integration of digital platforms and artificial intelligence (AI) stands as a major development. These platforms allow for automating some testing processes. Take, for instance, AI systems that detect chemical residues in food samples. Such systems not only speed up the process but they also enhance accuracy, eliminating human errors.
Secondly, the advent of portable testing devices is making waves. With such devices, chemical residue testing doesn’t have to be confined within the walls of a laboratory. The portability enables on-spot testing, which can be notably useful in remote areas.
Thirdly, advancements in blockchain technology might pave the way for increased transparency and traceability in food testing. Blockchain platforms can offer a tamper-proof record of all tests performed on a particular food item, ensuring the utmost integrity of data.
Lastly, environmentally friendly testing methods could become increasingly popular, given the growing emphasis on sustainability. More labs might opt for green chemistry protocols, which are testing methods that reduce or eliminate chemical hazards.
However, the successful adoption of these technologies hinges on overcoming several hurdles. Adequate funding, regulatory approvals, and well-coordinated international cooperation are just a few of the challenges that need to be addressed.
To sum up, I believe technology holds immense promise for the future of chemical residue testing in food. From AI to portable devices, blockchain, and green chemistry, these emerging trends have the potential to redefine food safety standards and practices globally.