Farm operators play a critical role in ensuring the safety of the food supply. From the initial stages of crop cultivation to the final stages of harvesting, their practices directly impact the potential for contamination. In Houston, recent E. coli outbreaks have highlighted the importance of robust safety measures and vigilant monitoring on farms to prevent the spread of harmful bacteria.
Understanding how farm operators contribute to these outbreaks is essential for implementing effective prevention strategies. This article will explore various aspects of farm operations that can lead to E. coli contamination, emphasizing the need for rigorous safety protocols and the role of regulatory oversight in maintaining food safety. For those affected by these outbreaks, understanding the origins and mechanisms of contamination is crucial, and consulting a lawyer for Houston E. coli infection cases can provide guidance and support in seeking justice and compensation.
Sources of E. Coli Contamination on Farms
One of the primary sources of E. coli contamination on farms is the use of contaminated water for irrigation. Water can become contaminated with E. coli from nearby livestock operations, sewage leaks, or runoff from fields treated with manure. When this water is used to irrigate crops, it can transfer bacteria onto the produce, posing a significant health risk.
Another common source is the improper handling and storage of manure. Manure, often used as fertilizer, can be a rich source of E. coli if not properly treated and managed. If manure comes into direct contact with crops or is used on fields too close to harvest time, it can contaminate the produce. Farm operators must follow stringent guidelines to ensure that manure is composted correctly and applied in a way that minimizes the risk of contamination.
Impact of Animal Proximity on Crop Safety
Proximity to livestock and wildlife can also increase the risk of E. coli contamination in crops. Animals can carry E. coli in their intestines, and their feces can spread the bacteria onto nearby crops. Farm operators need to implement measures to keep animals away from fields and to manage wildlife effectively to reduce this risk.
Fence installations and regular monitoring of the fields can help keep livestock and wild animals at a safe distance from crops. Additionally, creating buffer zones between animal grazing areas and crop fields is a crucial step in preventing contamination. These measures ensure that any bacteria carried by animals do not have a direct pathway to the produce.
Key Sanitation Practices for Farm Workers to Prevent E. Coli Contamination
Proper sanitation among farm workers is crucial to prevent the spread of E. coli and ensure the safety of produce. Workers who handle crops directly can inadvertently transfer bacteria, making strict hygiene practices essential. 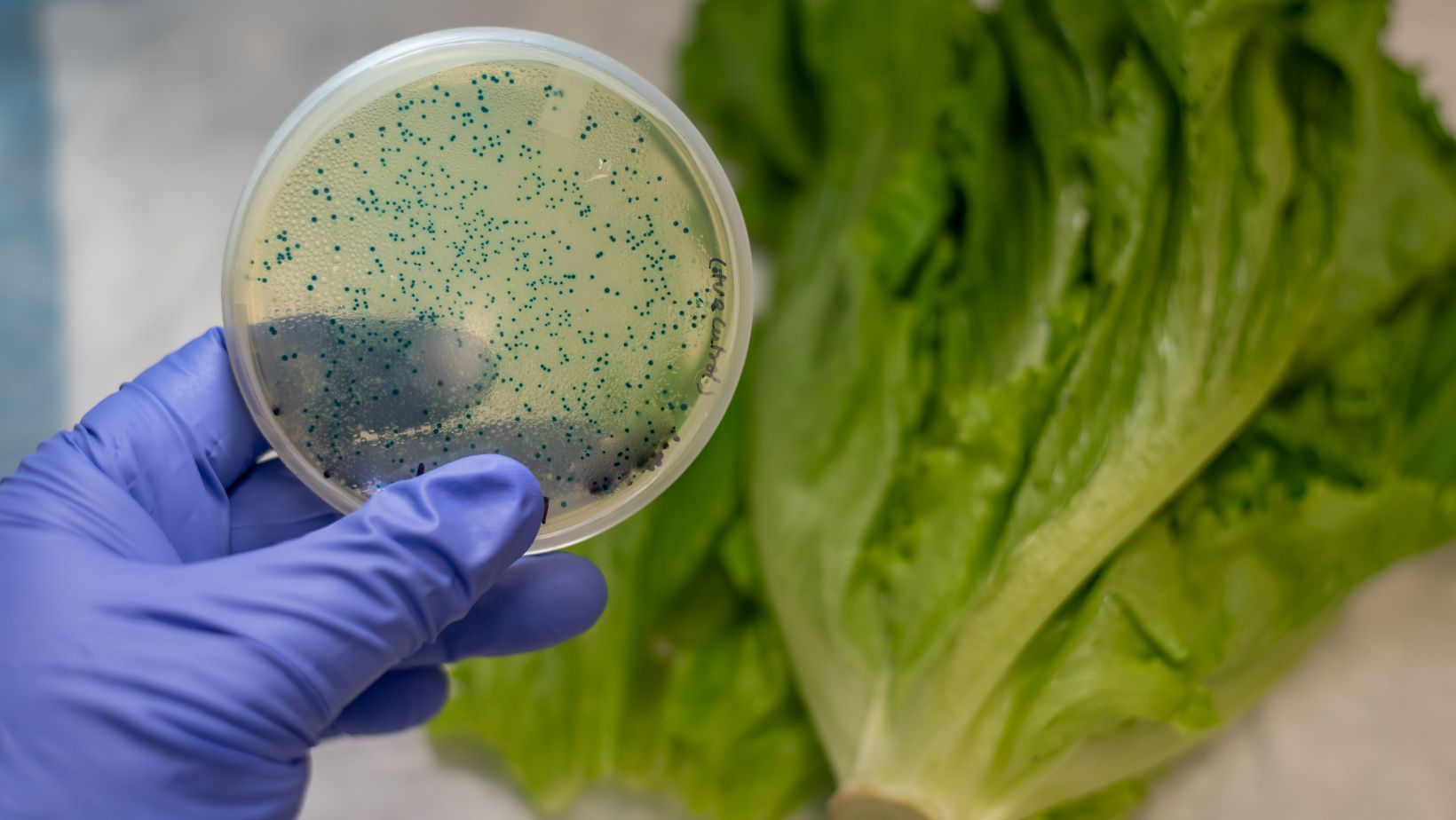
Adequate Handwashing Facilities:
Providing easily accessible handwashing stations equipped with soap, clean water, and disposable towels is essential. These facilities should be strategically placed throughout the farm to encourage regular use by all workers.
Regular Hygiene Training:
Continuous education on proper sanitation practices and the importance of hand hygiene is vital. Farm workers should receive training on effective handwashing techniques and be reminded of critical times for washing, such as before handling produce and after restroom use.
Encouraging Consistent Handwashing:
Establishing policies that mandate thorough handwashing before starting work, after breaks, and when handling crops can reduce contamination. Visible reminders around the farm can reinforce these practices, helping to maintain a high level of hygiene throughout the workday.
Post-Harvest Handling and Processing Risks
The post-harvest handling and processing of produce can also be a critical point where contamination occurs. If produce is washed with contaminated water or handled with unclean equipment, E. coli bacteria can be introduced to the food. This stage requires meticulous attention to cleanliness and proper sanitation protocols.
Ensuring that all equipment is regularly cleaned and sanitized and that water used for washing produce is safe and clean are vital steps in preventing contamination. Farm operators should establish strict protocols for post-harvest handling and regularly test water sources to ensure they are free from E. coli and other pathogens.
Regulatory Compliance and Oversight
Adhering to regulatory guidelines is crucial for farm operators to maintain food safety. Regulations such as the Food Safety Modernization Act (FSMA) provide standards that help prevent contamination. Compliance with these regulations requires regular inspections and audits, which can identify potential risks and ensure that farms maintain high safety standards.
Farm operators should stay updated on the latest regulatory requirements and seek regular training to understand and implement best practices. Partnering with food safety experts can also help farms achieve compliance and enhance their safety protocols, ultimately reducing the risk of E. coli outbreaks.
Role of Technology in Monitoring and Prevention
Advances in technology offer new tools for monitoring and preventing E. coli contamination on farms. Sensors and drones can be used to monitor water quality, detect contamination sources, and oversee the implementation of safety measures across large farming operations. These technologies can provide real-time data and early warning signs of potential contamination issues.
Implementing these technologies can help farm operators quickly identify and address risks before they lead to outbreaks. Investment in modern monitoring tools is a proactive step that enhances food safety and protects consumers from the dangers of E. coli.
Community and Consumer Education
Educating the community and consumers about the risks of E. coli and safe food handling practices is an important aspect of prevention. By raising awareness about how contamination occurs and what can be done to prevent it, farm operators and health authorities can foster a culture of safety and vigilance.
Farmers’ markets, community events, and educational programs can serve as platforms to disseminate information about E. coli prevention. Encouraging consumers to wash produce thoroughly and handle food safely can complement the safety measures taken on farms, creating a comprehensive approach to reducing the risk of E. coli infections.
By understanding and addressing the various ways farm operations contribute to E. coli outbreaks, stakeholders can work together to improve food safety and protect public health.