Industrial cooling systems are integral to manufacturing and processing operations. They help maintain desired temperature conditions, ensuring product quality and workplace safety. Condensers, in particular, play a crucial role in these systems by removing heat from the refrigerant. As we delve into the complexities of these components, you will gain a clearer understanding of their importance and functionality. Keep reading to explore how condensers sustain industrial cooling processes.
Exploring the Fundamentals of Industrial Cooling Systems

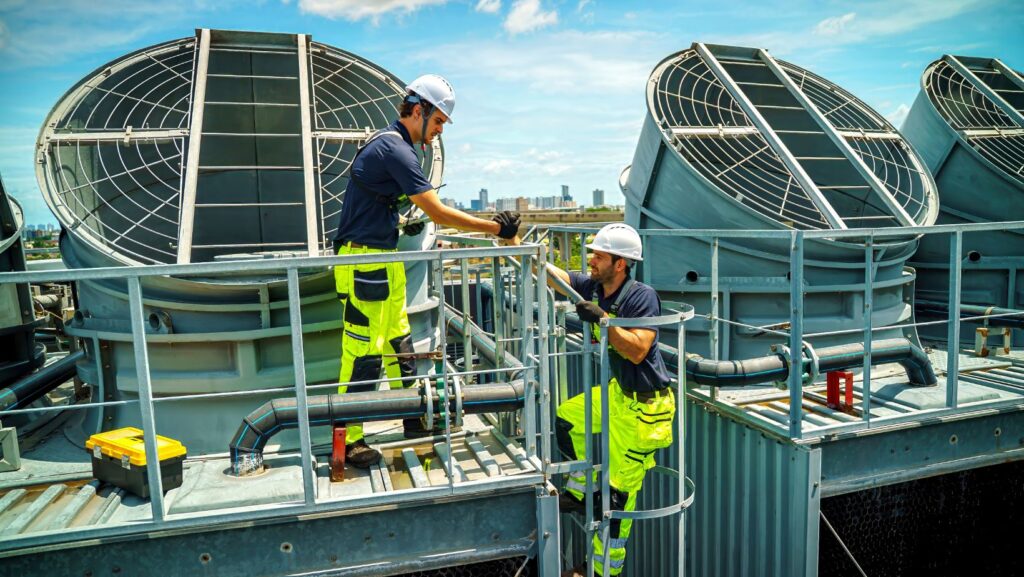
Industrial cooling systems manage large-scale heat loads in sectors like food processing, chemical production, and power generation. They rely on a precise refrigeration cycle to maintain consistent temperatures, ensuring operational safety and efficiency. Key components include compressors, evaporators, and condensers, each driving the flow and transformation of the refrigerant. The compressor raises the refrigerant’s pressure and temperature, preparing it for heat release.
In the condenser, the high-temperature refrigerant transfers its heat to air or water, condensing into a liquid ready to recirculate through the system. This process keeps industrial equipment operating within strict temperature limits. Condensers for industrial cooling are central to this cycle, efficiently removing unwanted heat and ensuring stable performance, regardless of system size or complexity.
How Condensers Function Within Industrial Refrigeration
Condensers play a vital role in the refrigeration cycle, acting as the point where refrigerants release heat and transition from gas to liquid. In industrial systems, they are engineered to manage high thermal loads, with coil design and surface area directly impacting heat transfer efficiency. The interaction between the refrigerant and the cooling medium, typically air or water, determines how effectively heat is dissipated, influencing the performance of the entire cooling system.
Maintaining optimal condenser operation is critical, with factors like ambient temperature, airflow, and coil cleanliness affecting efficiency. Industrial condensers are designed in varied capacities and configurations to meet specific operational demands, ensuring precise temperature control and reliable system performance across diverse industrial applications.
Key Types of Condensers and Their Industrial Applications
Condensers in industrial settings are primarily classified as air-cooled or water-cooled. Air-cooled condensers use ambient air to dissipate heat, making them ideal for smaller systems or areas with limited water resources. Their straightforward design reduces installation and maintenance costs. Water-cooled condensers, by contrast, employ water as a cooling medium, offering greater efficiency for large-scale operations. They are commonly used in power plants, chemical processing facilities, and expansive food refrigeration warehouses where substantial heat loads must be managed.
Within these categories, variations such as shell-and-tube, shell-and-coil, and plate condensers address specific industrial needs. Selection depends on factors like space constraints, refrigerant type, ambient conditions, and energy efficiency. Proper condenser choice enhances cooling system performance and operational reliability, making it a critical consideration for engineers and facility managers when designing or upgrading industrial cooling infrastructure.
Optimizing Efficiency: Best Practices for Condenser Maintenance

Proper maintenance of condensers is essential for industrial cooling system efficiency and longevity. Regular inspections and cleaning prevent dirt and debris buildup on condenser coils, ensuring optimal heat transfer. Monitoring refrigerant levels is equally critical, as leaks reduce performance and pose environmental risks. Prompt leak repairs and accurate refrigerant charging maintain system efficiency while complying with regulations.

Maintaining adequate airflow through air-cooled condensers is also vital. Obstructions or malfunctioning fans increase energy use and reduce performance, so ensuring clear air intake and exhaust is necessary. Routine inspection of other components, including compressors and evaporative condensers, helps detect issues that impact condenser operation, preventing costly downtime and repairs.
Technological Advancements and the Future of Industrial Condensing Systems
Technological advancements are transforming industrial condensers, with smart sensors and controls enabling real-time performance monitoring and predictive maintenance. These systems can detect potential issues early, ensuring uninterrupted operation while boosting energy efficiency. Innovations in materials and engineering are enhancing heat transfer and creating compact, high-efficiency designs that meet the growing demand for space-saving solutions in urban industrial settings.
Environmental and sustainability considerations are also shaping condenser development. Eco-friendly refrigerant compatibility addresses stricter regulations, while integrating renewable energy, such as solar-powered condensers, reduces operational costs and carbon emissions. These trends highlight the industry’s focus on efficiency, sustainability, and innovative approaches to modern industrial cooling technology.
Altogether, the functional and economic significance of condensers in industrial cooling should not be underestimated. With their continuous evolution, driven by technological advancements and sustainability efforts, condensers are set to remain a cornerstone in the effectiveness of industrial cooling systems.